Biomass Has so Much to Offer, Given the Right Approach
We develop and refine processes to efficiently valorise biomass. We can work on individual stages of a process, or develop a bespoke vertically-integrated technology based on your feedstock or desired end-product. This can be done at lab-scale up to the 100 litre level. Our in-depth understanding of biomass chemistry, our extensive array of bioprocessing equipment, and the biological, engineering, and commercial experience of our Bioprocess team, all play crucial roles in ensuring that our projects are well-designed and focused on our clients' end-goals.
Accurate data are not enough. We have in-depth understanding of the implications of composition and can design processes to fully valorise biomass.

|
|

|
|||||
Through innovation, passion, and determination, we at Celignis strive to make a difference in the development of the bioeconomy.
Looking for the Best Use for a Feedstock?
We have all the necessary analytical and bioprocess equipment, coupled with the expertise of our team, to undertake comprehensive projects for feedstock valorisation. We provide detailed reports which include key summaries of our findings.
Are you Targeting a Product and Need Help in Selecting the Feedstock and Process?
A large array of chemicals and materials are possible from biomass and wastes. These can involve chemical or biological approaches, or a combination of the two. Based on your desired end-product we can design and test the most appropriate bioprocess.
Want to Improve Your Existing Process?
We can undertake a detailed review of your existing bioprocess and identify key nodes where the process can be improved according to various metrics (yields, titres, purity, chemical use etc.). We then design a series of experiments to achieve the targeted objectives. These conditions can then be replicated at higher TRL levels.
How our Bioprocess Projects Work
We work closely with you to understand your objectives and timelines. We then propose a project, usually covering a series of deliverables and stage-gates. Often our projects involve optimising conditions at the lab-scale before replicating the conditions at higher TRL levels.
Global Recognition as Biomass Experts
Celignis provides valued services to over 1000 clients across the globe. We know how the focus of projects can differ between countries and have customs-exemptions for samples sent to us, allowing us to quickly get to work no matter where our clients are based.
We are proud of the knowledge, passion, and work ethic of our team. They have played key roles in the formulation, optimisation, and commercial evaluation of bioprocesses.

Lalitha Gottumukkala
Founder of Celignis Bioprocess, CIO of Celignis
PhD
<p style="text-align: left;">Has a deep understanding of all biological and chemical aspects of bioproceses. Has developed Celignis into a renowned provider of bioprocess development services to a global network of clients.</p>

Oscar Bedzo
Bioprocess Project Manager & Technoeconomic Analysis Lead
PhD
<p style="text-align: left;">A dynamic, purpose-driven chemical engineer with expertise in bioprocess development, process design, simulation and techno-economic analysis over several years in the bioeconomy sector.</p>

Dan Hayes
Celignis CEO And Founder
PhD (Analytical Chemistry)
<p style="text-align: left;">Dreamer and achiever. Took Celignis from a concept in a research project to being the bioeconomy's premier provider of analytical and bioprocessing expertise.</p>

Sajna KV
Bioanalysis Developer
PhD
<p style="text-align: left;">Our Biomass Detective! Designs, tests, optimizes and validates robust analytical methods for our bioprocess development projects. Such bespoke analysis is key to developing an optimised bioprocess.</p>

Piotr Dobkowski
Orders and Data Manager
MAc
<p style="text-align: left;">Feeds on quality data! Piotr plays a major role in data processing and Orders management at Celignis and is responsible for ensuring bioprocess data are rapidly uploaded to the Celignis Database.</p>


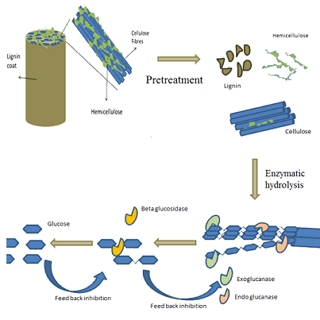
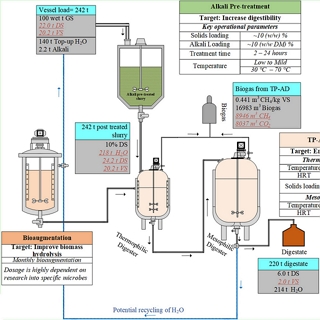
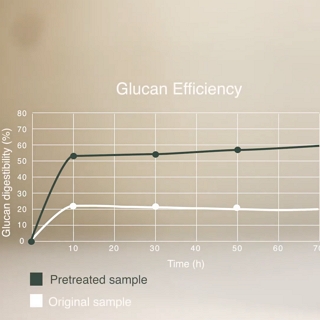
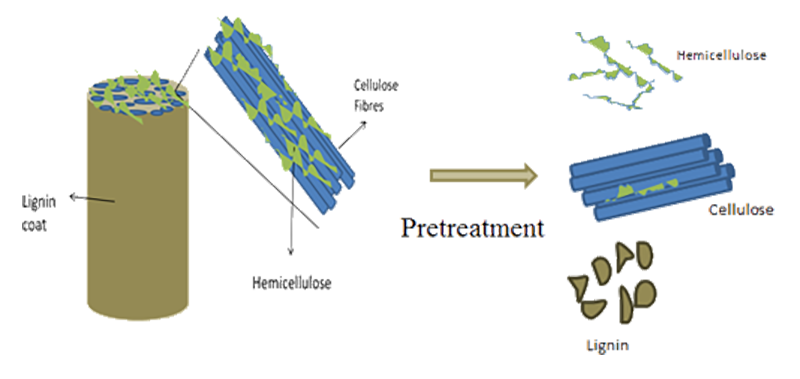
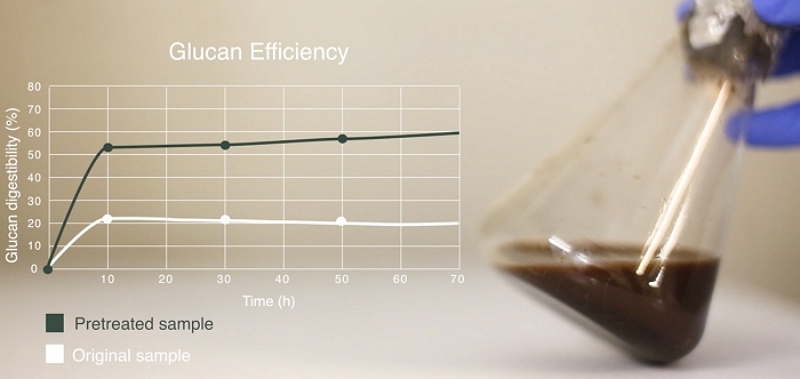
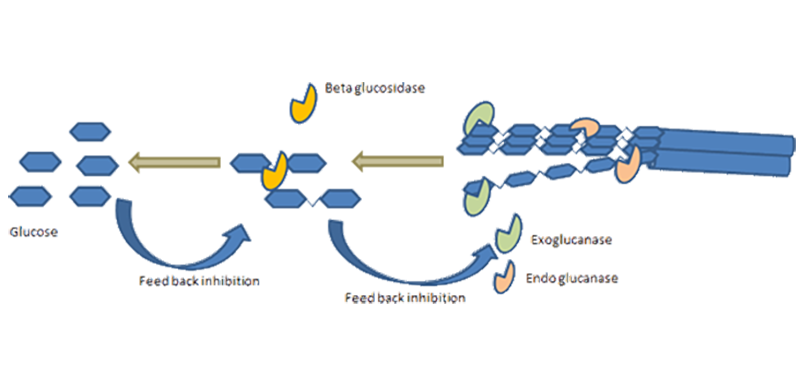
The project involved a series of lab-scale experiments focused on optimising the pretreatment conditions so that the yields and commercial viability of the process as a whole could be improved. The next stage of the project then involved optimising the type and dosage of enzymes, as well as other factors such as the solid-loading, in order to maximise ethanol yields from the targeted biomass components.
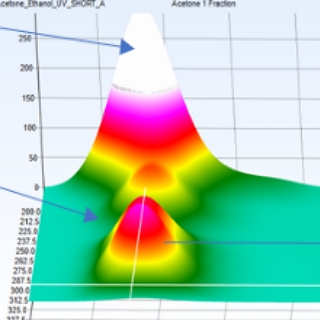
The target of the project were polymers of improved properties for application in a variety of different biomaterials applications. We found that tweaks in the extraction and modification stages of the bioprocess could influence the physicochemical properties of the resuting alginate and could allow the process to be tailored for producing different types of materials for different end-uses.
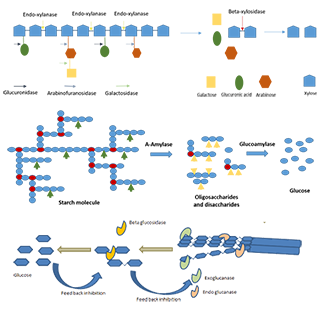
The project involved examining a number of important process variables, including: pretreatment conditions; the type and loading of enzymes; and the duration and conditions of the hydrolysis stage. The final outputs of the project were selected optimum conditions for each of the examined feedstock types and recommendations for further optimisations of the process and future scaled-up activities.
Optimising the bioprocess required a carefully-formulated DoE considering relevant factors (e.g. temperature, enzymes, pretreatment) in the context of the chosen feedstock and the final product requirements. In all such projects that we have undertaken to date we developed an improved bioprocess that allowed for greater proportions of the total carbohydrates in the liquid phase being in the client's targeted product range.
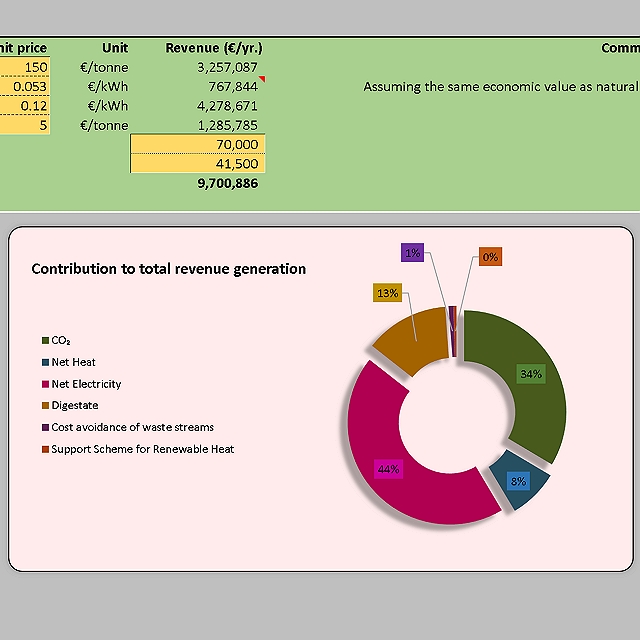
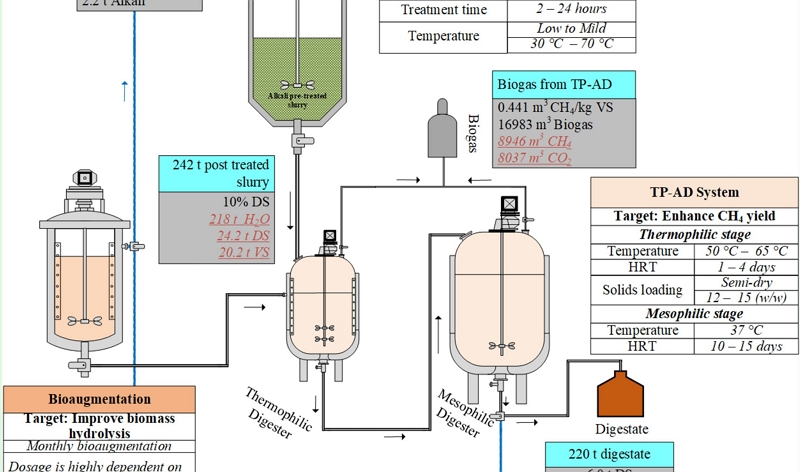
Following the completion of our lab-scale work, we worked on a technoeconomic analysis of the bioprocess, considering several different scenarios. These included the scale-up of the process as-developed as well as the modelling of the process after several modifications (e.g. simultaneous saccharification and fermentation (SSF) rather than separate hyrolysis and fermentation ( SHF)).
The outputs of this TEA informed a follow-on bioprocess development project, incorporating the changes deemed to give greatest impact to the process in terms of commercial and environmental sustainability.