Analysis of Glycosides
Background
Glycosides are a class of organic compounds in which a sugar molecule is bound to a non-sugar molecule,
known as an aglycone or genin. The sugar component can be a single sugar (monosaccharide) or a chain of sugars
(oligosaccharide), and the non-sugar component can be any other molecule, often a lipid or a protein.
This bond between the sugar and non-sugar component is known as a glycosidic bond.
Glycosides are prevalent in nature and are found in a wide range of plants. They serve a variety of functions depending on their structure and the specific plant in which they are found. For instance, they can act as a form of energy storage, be involved in plant defense, or play a role in pigmentation.
Glycosides are prevalent in nature and are found in a wide range of plants. They serve a variety of functions depending on their structure and the specific plant in which they are found. For instance, they can act as a form of energy storage, be involved in plant defense, or play a role in pigmentation.
There are many types of glycosides, which are usually categorized based on their non-sugar component. A few examples are
listed below:
- Anthocyanins - These are glycosides of anthocyanidins, a type of flavonoid, and are responsible for the red, purple, and blue colors found in many fruits and flowers.
- Cardiac Glycosides - These are a class of organic compounds that have the ability to increase the output force of the heart and decrease its rate of contractions. They have been used for many years in the treatment of congestive heart failure and arrhythmia.
- Saponins - These are glycosides that form a soapy froth when shaken in water. They have a wide range of properties and uses, from their role as natural detergents to their potential health benefits due to their antioxidant and immune-boosting activities.
- Cyanogenic Glycosides - Found in a number of plants, these glycosides can release hydrogen cyanide when the plant tissue is damaged, acting as a defense mechanism against herbivores.
Glycosides in Different Types of Biomass
Examples of some common glycosides found in bark are provided below:
Get more info...Bark
- Salicin - Found in the bark of willow trees and has pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory properties. Once ingested, salicin is converted into salicylic acid in the body. This compound served as the initial inspiration for the synthesis of acetylsalicylic acid, better known as aspirin.
- Arbutin - This glycoside is found in the bark of a number of tree species, including the bearberry tree. Arbutin has been used in traditional medicine for urinary tract health, and it is also used in cosmetic products due to its skin-lightening properties.
- Paeoniflorin - Present in the bark of the tree peony, it is known for its potential anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and neuroprotective properties.
- Amygdalin - A cyanogenic glycoside found in the bark and seeds of several plants, including some types of fruit trees.
- Oleuropein - Found in the bark (and leaves) of olive trees, it has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties and has been studied for potential health benefits related to heart health and blood sugar regulation.
- Aesculin - A coumarin glycoside that is found in the bark of the horse chestnut tree. Aesculin has various potential health benefits, including anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.
Get more info...Bark
Examples of some common glycosides found in roots are provided below:
Get more info...Roots
- Saponins - These are glycosides that form soap-like foams when mixed with water. They are found in a wide variety of plants, including the roots. Some saponins, like those found in ginseng or licorice roots, have been studied for a variety of health effects, including immune-boosting and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Glycyrrhizin - This glycoside is found in the roots of the licorice plant. It is much sweeter than sugar and has been used in food and traditional medicine. It has anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating effects, but excessive consumption can lead to side effects like high blood pressure.
- Salicin - While mostly found in the bark of willow trees, it is also present in their roots.
- Digoxin - This cardiac glycoside is found in the roots of the Digitalis (foxglove) plant. It is used in medicine to treat certain heart conditions, but must be used carefully due to its narrow therapeutic index and potential for toxicity.
- Stevioside - This is a sweet glycoside found in the roots and leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana plant. It's used as a non-caloric sweetener.
Get more info...Roots
Examples of some types of glycosides found in seeds are listed below:
Get more info...Seeds
- Cyanogenic Glycosides - hese are found in several types of seeds, including apple seeds, peach pits, and apricot kernels. When these seeds are chewed or digested, the cyanogenic glycosides can release cyanide, which can be toxic in high amounts. However, the small amounts in these seeds are generally not harmful unless consumed in very large quantities.
- Cardiac Glycosides - These are found in the seeds and leaves of some plants like foxglove (Digitalis purpurea). They have been used in medicine to help regulate heart function.
- Flavonoid Glycosides - Common in a variety of seeds. For example, quercetin glycosides, a type of flavonoid glycoside, can be found in onion seeds.
- Saponin Glycosides - Found in many types of seeds, including quinoa and soybeans. They have a variety of potential health benefits but can also interfere with nutrient absorption in large amounts.
- Anthraquinone Glycosides - Present in the seeds of certain plants like senna and rhubarb. They have a laxative effect and are used in some herbal remedies for constipation.
- Glucosinolates - Sulphur-containing glycosides found in the seeds of cruciferous vegetables like mustard, broccoli, and cabbage. They can break down into various compounds with potential health benefits, including indoles and isothiocyanates.
Get more info...Seeds
Extraction of Glycosides from Biomass
The extraction process, including the solvents and methods used, can influence the concentration and types of glycosides present in the final extract.
It is often the case that a balance needs to be found between fully-extracting all glycosides while also ensuring that the compounds that are
obtained are of a high quality and not degraded.
At Celignis we have extensive experience in the design and optimisation of extraction protocols for a wide variety of chemical constituents from many different biomass types. If needed we can also work on processes to separate and purify the target compounds.
Click here to read more about Celignis's Bioprocess Development Services for the extraction of chemicals from biomass.
Get more info...Biomass Extractions
At Celignis we have extensive experience in the design and optimisation of extraction protocols for a wide variety of chemical constituents from many different biomass types. If needed we can also work on processes to separate and purify the target compounds.
Click here to read more about Celignis's Bioprocess Development Services for the extraction of chemicals from biomass.
Get more info...Biomass Extractions
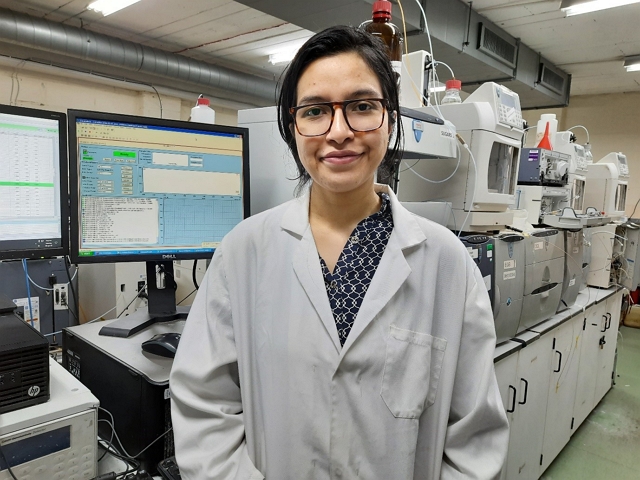
Analysis of Glycosides at Celignis
We have the necessary equipment and expertise to determine the amount and distribution of glycosides in
a wide variety of biomass samples.
Feel free to get in touch with us to request further information and a quotation.
Request a QuoteGlycosides Analysis
Feel free to get in touch with us to request further information and a quotation.
Request a QuoteGlycosides Analysis