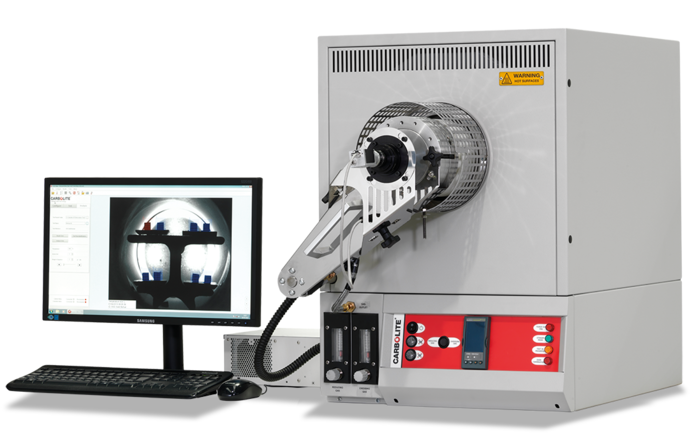
The method of analysing for ash melting behaviour involves heating the ash up in a controlled manner and determining a number of characteristic temperatures at which the ash will begin to deform, soften, and completely deform or fuse into a blob.
With this new equipment, and the analysis packages it enables, we can monitor the degradation characteristics of the ash (from 600 to 1550C) using a digital camera that takes an image for every 1C increase in temperature. This allows us to provide data for the following specific ash fusion characteristic temperatures:
- Ash Shrinkage Starting Temperature
- Ash Deformation Temperature
- Ash Hemisphere Temperature
- Ash Flow Temperature
These tests can be run under oxidising or reducing conditions. We usually recommend that reducing conditions are used for biomass samples.
Click here to read more about this equipment and the analyses undertaken.