Analysis of MSW
Background on MSW
Many countries have targets for reducing the amount of biodegradable municipal waste that is sent to landfill. For example, the European Union's Landfill Directive (1999) sets progressive targets to reduce the amount of biodegradable municipal waste land-filled, when compared against the waste produced in the baseline year of 1995.
Incineration is one of the currently favoured methods for reducing the quantity of biodegradable municipal waste (and all municipal solid waste) that is sent to landfill. Biorefineries that can produce advanced biofuels (often termed cellulosic fuels) from organic materials are another option for valorising biodegradable municipal waste.
Celignis founder Daniel Hayes has considerable experience in the chemical and near-infrared analysis of MSW and has been involved in a research project, funded by the Irish Environmental Protection Agency, that involved collecting, preparing, and characterising a variety of MSW samples. Samples that have been analysed include the organic fraction of black bin wastes, brown-bin wastes, and wastes that have been treated by different MBT (mechanical and biological treatment) technologies. Daniel Hayes has also collected many samples of biomass/wastes that contribute to mixed biodegradable municpal waste and characterised these separately. Such samples include numerous papers and cardboards, as well as green wastes (e.g. lawn cuttings and tree trimmings).
Analysis of MSW at Celignis
Celignis Analytical can determine the following properties of MSW samples:
Lignocellulosic Properties of MSW
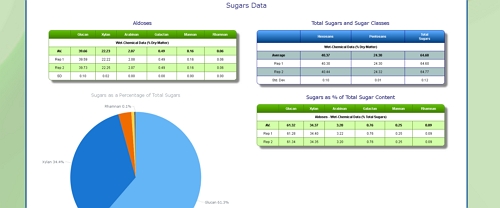
Cellulose Content of MSW
The chemical composition of MSW also varies significantly over the course of a year, with more green waste in periods when plant productivity is greatest. Food wastes will also vary according to changes in diet over the year.
Click here to see the Celignis Analysis Packages that determine Cellulose Content
Request a QuoteCellulose Content
Hemicellulose Content of MSW
Click here to see the Celignis Analysis Packages that determine Hemicellulose Content
Request a QuoteHemicellulose Content
Lignin Content of MSW
Click here to see the Celignis Analysis Packages that determine Lignin Content
Request a QuoteLignin Content
Starch Content of MSW
Click here to see the Celignis Analysis Packages that determine Starch Content
Request a QuoteStarch Content
Uronic Acid Content of MSW
As a result of this, uronic acid content of MSW is likely to vary throughout the year and according to location and diet.
Click here to see the Celignis Analysis Packages that determine Uronic Acid Content
Request a QuoteUronic Acid Content
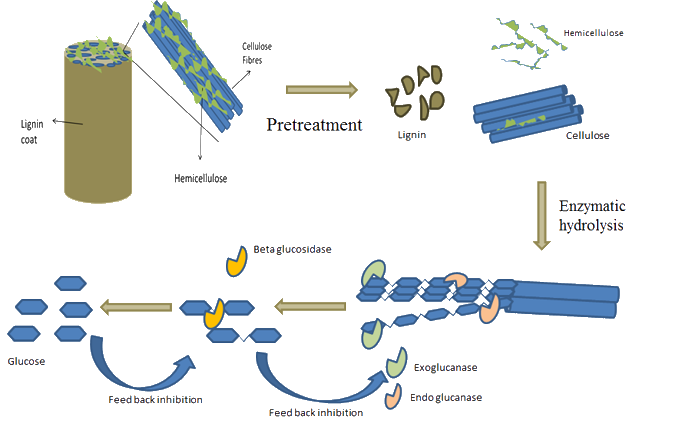
Enzymatic Hydrolysis of MSW
Click here to see the Celignis Analysis Packages that determine Enzymatic Hydrolysis
Request a QuoteEnzymatic Hydrolysis
Bioenergy Properties of MSW
Ash Content of MSW
Click here to see the Celignis Analysis Packages that determine Ash Content
Request a QuoteAsh Content
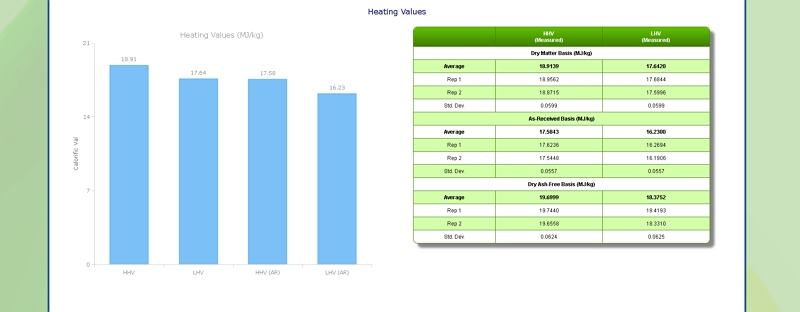
Heating (Calorific) Value of MSW
Click here to see the Celignis Analysis Packages that determine Heating (Calorific) Value
Request a QuoteHeating (Calorific) Value
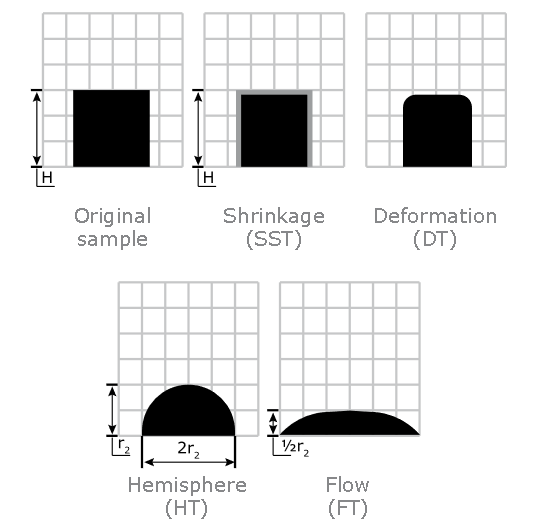
Ash Melting Behaviour of MSW
Ash Shrinkage Starting Temperature (SST) - This occurs when the area of the test piece of MSW ash falls below 95% of the original test piece area.
Ash Deformation Temperature (DT) - The temperature at which the first signs of rounding of the edges of the test piece occurs due to melting.
Ash Hemisphere Temperature (HT) - When the test piece of MSW ash forms a hemisphere (i.e. the height becomes equal to half the base diameter).
Ash Flow Temperature (FT) - The temperature at which the MSW ash is spread out over the supporting tile in a layer, the height of which is half of the test piece at the hemisphere temperature.
Click here to see the Celignis Analysis Packages that determine Ash Melting Behaviour
Request a QuoteAsh Melting Behaviour
Major and Minor Elements in MSW
We can also determine the levels of 13 different minor elements (such as arsenic, copper, and zinc) that may be present in MSW.
Click here to see the Celignis Analysis Packages that determine Major and Minor Elements
Request a QuoteMajor and Minor Elements
Analysis of MSW for Anaerobic Digestion
Biomethane potential (BMP) of MSW
At Celignis we can provide you with crucial data on feedstock suitability for AD as well as on the composition of process residues. For example, we can determine the biomethane potential (BMP) of MSW. The BMP can be considered to be the experimental theoretical maximum amount of methane produced from a feedstock. We moniotor the volume of biogas produced allowing for a cumulative plot over time, accessed via the Celignis Database. Our BMP packages also involve routine analysis of biogas composition (biomethane, carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulphide, ammonia, oxygen). We also provide detailed analysis of the digestate, the residue that remains after a sample has been digested. Our expertise in lignocellulosic analysis can allow for detailed insight regarding the fate of the different biogenic polymers during digestion.
Click here to see the Celignis Analysis Packages that determine BMP
Request a QuoteBMP
Physical Properties of MSW
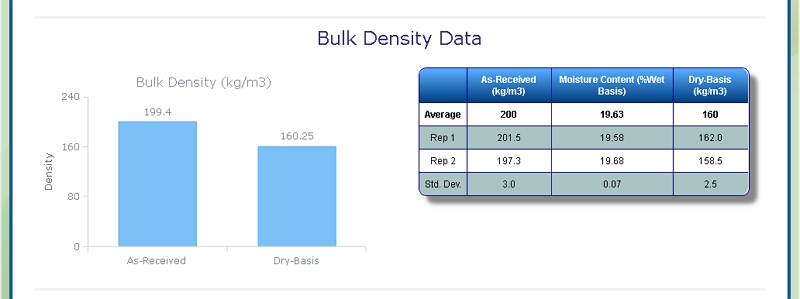
Bulk Density of MSW
At Celignis we can determine the bulk density of biomass samples, including MSW, according to ISO standard 17828 (2015). This method requires the biomass to be in an appropriate form (chips or powder) for density determination.
Click here to see the Celignis Analysis Packages that determine Bulk Density
Request a QuoteBulk Density
Particle Size of MSW
Our lab is equipped with a Retsch AS 400 sieve shaker. It can accommodate sieves of up to 40 cm diameter, corresponding to a surface area of 1256 square centimetres. This allows us to determine the particle size distribution of a range of samples, including MSW, by following European Standard methods EN 15149- 1:2010 and EN 15149-2:2010.
Click here to see the Celignis Analysis Packages that determine Particle Size
Request a QuoteParticle Size
Waste pulp was recovered from MRF rejects, purified, processed into paper sheets and laminated with polylactide (PLLA) films. The purification process employed produced waste pulp of different qualities. The mechanical properties of the resulting waste pulp fibre-reinforced laminated PLLA composites was indifferent to the type of waste pulp treatment used. All composites showed significant improvements over neat PLLA, highlighting the viability of using waste pulp as a potentially cheap and sustainable reinforcement for polymers. Lifecycle assessment further showed that the composites possessed lower net global warming potential, as well as the end-point impact categories of human health and ecosystem quality compared to neat PLLA. This is due to the higher mechanical performance of the composites, which leads to higher weight saving of the functional unit. Our work paves the way for the use of pulp rejects from the recycling process for higher value applications, diverting them from landfill or incineration. | |
The processing of lignocellulosic materials in modern biorefineries will allow for the
production of transport fuels and platform chemicals that could replace petroleum-derived
products. However, there is a critical lack of relevant detailed compositional information
regarding feedstocks relevant to Ireland and Irish conditions. This research has involved the
collection, preparation, and the analysis, with a high level of precision and accuracy, of a
large number of biomass samples from the waste and agricultural sectors. Not all of the
waste materials analysed are considered suitable for biorefining; for example the total sugar
contents of spent mushroom composts are too low. However, the waste paper/cardboard
that is currently exported from Ireland has a chemical composition that could result in high
biorefinery yields and so could make a significant contribution to Ireland’s biofuel demands. | ||